For farmers aiming to maximize crop yield and soil health, understanding soil composition through testing is essential. Soil analysis reveals crucial data about nutrient levels, pH, and other factors, allowing farmers to tailor their approach to meet the specific needs of their farmland. Studies show that optimized soil health can boost crop yield by up to 20%, which translates into a more efficient use of resources and a stronger bottom line.
Soil analysis also helps prevent the costly mistake of overusing fertilizers. Excessive fertilizer use can harm crops, waste money, and damage the environment. By testing soil, farmers get precise insights that support sustainable farming, targeted fertilization, protecting both their investment and the farmland.
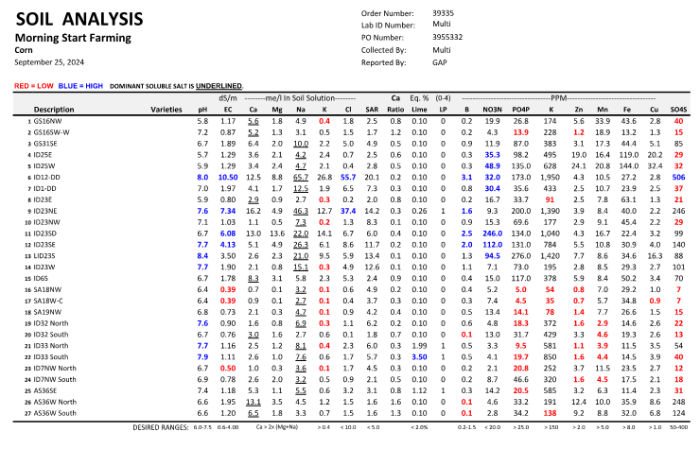
Understanding Soil Analysis Report Values
Farmers who want to get the most from their soil analysis report should know the common values listed. Here’s a breakdown of important soil characteristics, with explanations on how they affect crops.
Key Soil Analysis Values
Beneficial Levels:
- pH: A neutral pH of around 7 is ideal for most crops, promoting nutrient availability.
- Calcium (Ca): Essential for soil structure and plant cell strength, optimal levels improve resilience.
- Magnesium (Mg): Important for photosynthesis; an adequate level ensures plant health.
- Potassium (K): Supports water regulation and disease resistance, crucial for healthy growth.
Potentially Harmful Levels:
- Sodium (Na): High levels damage soil structure, impacting drainage and root development.
- Chloride (Cl): Beneficial in small quantities, but excess chloride can be toxic to plants.
- Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR): High SAR indicates risks of soil compaction, hindering water movement and root growth.
Additional Important Values
- Electrical Conductivity (EC): Reflects soil salinity; high EC can stress plants.
- Nitrate Nitrogen (NO3N): Vital for growth, but excessive nitrate can cause nutrient imbalances.
- Phosphate Phosphorus (PO4P): Key for root development; low levels stunt plant growth.
Download this soil analysis guide to learn more about interpreting each of these values.
Save Your Soil Data with AgNote
AgNote offers a convenient way for farmers to store soil analysis documents and other crop-related files. By keeping all records in one place, farmers can track and analyze trends over time, ensuring healthier soil and better yields. Register with AgNote today to manage your soil data more effectively!