Almond hulling is the process of removing the outer layer of the almond. The outer layer consists of the hull and the shell, in order to separate the edible kernel. This is a crucial step in almond production, as it affects the quality, safety, and marketability of the almonds. Almond hulling also generates by-products such as hulls, shells, and debris, which can be used for various purposes such as animal feed, mulch, fuel, and landfill.
The almond hulling process usually involves several steps, depending on the type of facility and equipment that is being used.
Typical Almond Hulling Steps

- Almond Shaking: Almonds are harvested in the fall. That’s when the hulls that cover the nuts split open and expose the shells. A machine shakes the tree and makes the nuts fall to the ground. Nuts stay on the ground for several days (7-10) where they dry.
- Sweeping and picking: When almond nut moisture is between 4-6% they are swept into rows and picked up by mechanical harvester (pickup). The picked almonds contain a mixture of nuts, hulls, shells, leaves, branches, soil, and gravels.
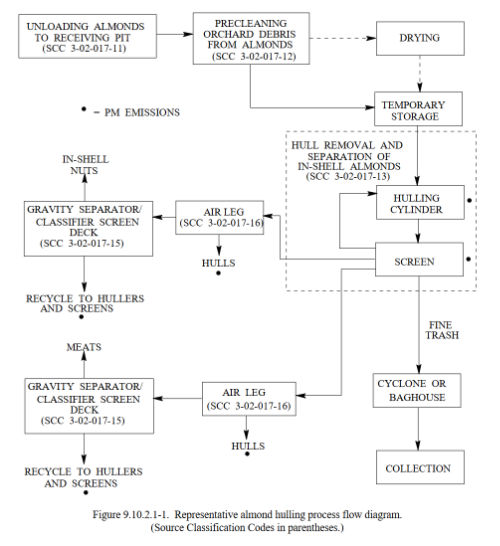
- Pre-cleaning: First pre-cleaning happens during the almond pickup and while loading them into trailer. Then almonds are transported to a pre-cleaning facility. There they are screened and separated from the large debris using machines such as de-stickers, de-stoners and de-twiggers. The pre-cleaned almonds are then stored in tanks until they are ready for hulling.
- Almond Hulling: The almonds are fed into a huller machine, which cracks the hulls and separates them from the nuts using rollers, beaters, and screens. The hulled nuts are then moved to a sheller machine or a huller/sheller machine.
- Shelling: The sheller machine or the huller/sheller machine breaks the shells and separates them from the kernels using impactors, crackers, and separators. The shelled kernels are then inspected for quality control and sorted by size and grade.
- Processing: The shelled kernels are then transported to a processing facility, where they may undergo further processing such as blanching, roasting, slicing, or dicing, depending on the desired end-product.
Final Thoughts
For process flow chart enthusiasts, here is Almond Hulling Process diagram from US EPA.
Almond hulling process is a complex and efficient operation that requires specialized equipment and skilled workers. It also produces valuable by-products that can be utilized for various applications. The almond hulling process is an essential part of almond production that ensures high quality and safe almonds for consumers.
Other Almond Crop Management Resources
Here are some almond farming related blog posts:
- How to Prevent Almond Hull Rot and Boost Your Crop Yield
- What Is Almond Hull Split and Why Is It Important for Growers?
- Why Is Almond Orchard Sanitation So Very Important?
- Permanent Crop Management
If you are an almond grower and are exploring practical tools which would help you with almond orchard data management, please check out AgNote. Now you can register for free seven-day trial and test it yourself on how AgNote will help you with permanent crop season management.