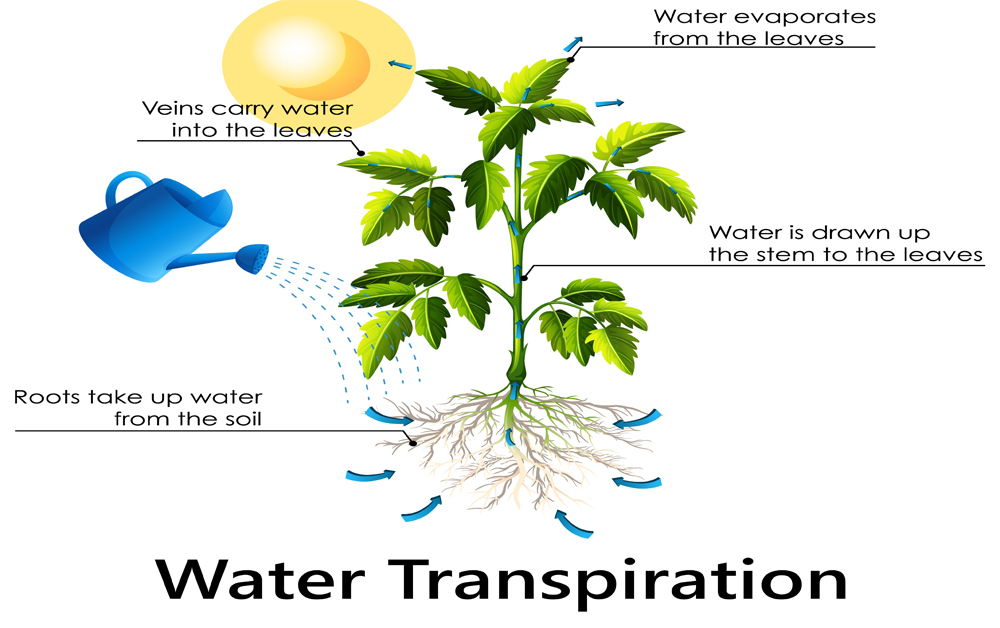
Water transpiration is a vital process in plants that supports nutrient movement and temperature regulation. It occurs when water absorbed by the roots travels through the plant and evaporates from tiny pores on the leaves called stomata. This evaporation creates a suction effect, drawing water and dissolved nutrients upward from the soil. Without transpiration, plants cannot efficiently distribute essential minerals or cool themselves, which are critical for growth and survival.
Soil type plays a significant role in water transpiration. Sandy soils, for example, drain water quickly, which can increase transpiration as plants work harder to uptake moisture. Clay soils retain water longer, slowing down the rate of water loss through evaporation and plant uptake. Loamy soils offer a balanced environment for optimal water retention and airflow, making them ideal for consistent plant transpiration.
Factors Influencing Water Transpiration Rates in Farming
Several factors can directly influence the rate of water transpiration in crops, ranging from environmental conditions to plant traits. Managing these factors can improve water efficiency on farms.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase evaporation and transpiration rates.
- Humidity: Lower humidity accelerates transpiration as drier air pulls moisture from leaves.
- Wind Speed: Wind removes moisture from leaf surfaces, increasing transpiration.
- Soil Moisture: Limited water in the soil reduces a plant’s ability to transpire.
- Plant Type: Plants with smaller leaves or thick waxy coatings transpire less water.
The Role of Water Transpiration in Crop Growth and Climate Adaptation
It plays a vital role in ensuring crop health and development by facilitating nutrient absorption and distribution. Through this process, plants draw water and nutrients from the soil, transporting them to leaves and other parts essential for growth. This mechanism supports photosynthesis, enhances metabolic functions, and promotes overall plant vigor, ensuring crops reach their full potential.
In addition to its growth-related benefits, transpiration offers a natural cooling effect that shields plants from heat stress, particularly during periods of high temperatures. As climate conditions grow more unpredictable, efficient transpiration helps crops adapt to challenges like prolonged droughts or sudden temperature spikes. By maintaining these physiological processes, plants can sustain productivity and improve resilience in changing environments.
Best Practices to Manage Water Transpiration for Improved Yield
- Mulching: Conserves moisture and reduces evaporation.
- Drip Irrigation: Directly supplies water to plant roots, improving efficiency.
- Windbreaks: Protect fields from wind to reduce excessive water loss.
- Optimizing Soil Quality: Enhance soil’s water-holding capacity with organic matter.
- Crop Selection: Choose crops adapted to specific soil and climate conditions.
Optimize Your Water Management with AgNote for Better Crop Yield
AgNote simplifies farm management by providing tools to monitor water usage, soil health, and crop conditions. With real-time analytics, farmers can make data-driven decisions to optimize irrigation and manage water transpiration effectively. Start your 7-day free trial with AgNote today and take control of your farm’s water efficiency.